Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hokama, Tomonori; Kimura, Masanori; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Research 2023-010, 57 Pages, 2024/02
In the case of a nuclear accident, itis planned to perform simple measurement of radioactive iodine radioactivity in the thyroid of residents. The screening level for simple measurement is set at 0.20  Sv/h as a reference, and it is required to be reviewed appropriately according to the situation such as a nuclear accident. However, a specific method for reviewing the screening level is not shown. When reviewing the screening level, it is important to take into account factors related to the feasibility of simple measurement, such as the judgment level for internal exposure dose of the thyroid and the duration of the measurement period. In this study, we organized the derivation process of 0.20
Sv/h as a reference, and it is required to be reviewed appropriately according to the situation such as a nuclear accident. However, a specific method for reviewing the screening level is not shown. When reviewing the screening level, it is important to take into account factors related to the feasibility of simple measurement, such as the judgment level for internal exposure dose of the thyroid and the duration of the measurement period. In this study, we organized the derivation process of 0.20  Sv/h, which was set as the reference for screening level, and considered the feasibility of the reviewing of screening level. We calculated the relationship between the judgment level and the duration of simple measurement for each screening level, ranging from 0.025 to 0.50
Sv/h, which was set as the reference for screening level, and considered the feasibility of the reviewing of screening level. We calculated the relationship between the judgment level and the duration of simple measurement for each screening level, ranging from 0.025 to 0.50  Sv/h. Then, the feasibility of the reviewing of screening level was considered. It was found that reviewing the screening level is technically feasible, provided that the judgment level and the duration of simple measurement are appropriate. However, assuming that simple measurement will be performed in an actual nuclear accident, we assessed that it would be reasonable to review the screening level within the range of 0.030 to 0.20
Sv/h. Then, the feasibility of the reviewing of screening level was considered. It was found that reviewing the screening level is technically feasible, provided that the judgment level and the duration of simple measurement are appropriate. However, assuming that simple measurement will be performed in an actual nuclear accident, we assessed that it would be reasonable to review the screening level within the range of 0.030 to 0.20  Sv/h, in a situation where the duration of simple measurement must be extended.
Sv/h, in a situation where the duration of simple measurement must be extended.
Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sato, Rina; Nakayama, Mariko*; Tsubokura, Masaharu*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 64(2), p.203 - 209, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Biology)After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident, individual exposure doses to residents have been assessed by many municipalities, governments and research institutes. Various methods including measurements with personal dosimeters and simulations have been used for this evaluation depending on purposes, but the information of assessments and methods has not been systematically organized. A comprehensive review of the knowledge and experiences of individual exposure doses assessments accumulated so far and understanding the characteristics of the assessment methods will be very useful for radiation protection and risk communication, following to governmental policy planning. We reviewed the efforts made by the Japanese government and research institutes to assess radiation doses to residents after the FDNPS accident in Part1. On the other hand, each method of assessing individual exposure doses includes uncertainties and points to be considered for the appropriate assessment. These knowledge and experiences are important for the assessment implementation and applying the assessment results to the governmental policy planning, and are summarized in Part2 of this article.
Shimada, Kazumasa; Iijima, Masashi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Takahara, Shogo
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2021 (ASRAM 2021) (Internet), 17 Pages, 2021/10
The radiation doses received by the off-site responders in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident were assessed. Atmospheric dispersion simulation was conducted with the source term of the previous research to calculate the atmospheric concentration and ground surface deposition in the municipalities where off-site responders actives. The external exposure dose from cloudshine and groundshine, the internal exposure dose due to inhalation of radioactive plume and resuspended radio nuclei, and the temporal and spatial distribution within each municipality were assessed. As a result of comparing the assessed values of the external exposure dose with the measured values of the personal dosimeter, the measured values were within the assessed range. As a result of our assessment with internal dose exposure, if the exposures occurred without protective measures, the potential daily effective dose in the period between 12 and 31 March 2011 were several tens mSv per day or more in the relatively high dose area. Therefore, to keep the doses received by the responders below the reference level of 20 mSv recommended by the ICRP, it is necessary to ensure that the protective measures for internal exposures such as masks are taken, and to manage the time spent for their activity at least daily.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Funaki, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Abe, Tomohisa; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Tanimori, Soichiro*; Sato, Rina
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(2), p.62 - 73, 2021/06
Japanese government starts to consider radiation protection in the "specific reconstruction reproduction base area" of which evacuation order will be lifted by 2023. It is essential to grab the present situations of radiation contamination and evaluate exposure dose in the area to realize the plan. Many surveys have evaluated the distributions of air dose rate and exposure dose has been estimated based on the results since the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Nevertheless, more detailed information on exposure is needed for the areas because its radiation level is relatively high. That is also to help make prudent evaluation plan. This study aimed to evaluate the detailed contamination situation there and estimate exposure dose with considering areal circumstances. Investigations were carried out for (1) airborne survey of air dose rate using an unmanned helicopter (2) evaluation of airborne radiocesium and (3) estimation of external/internal effective doses for typical activity patterns assumed.
Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Abe, Daichi*; Okada, Shota; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2021-004, 79 Pages, 2021/05
JAEA has aims to carry out near surface disposal of low-level radioactive waste generated from research, medical, and industrial facilities. Therefore, radioactivity concentration corresponding to dose criteria of near surface disposal for 220 nuclides in the waste were calculated for the purpose of discussion for radioactivity limits between trench and concrete vault disposal, and key nuclides related to them. We calculated the radioactivity concentrations with consideration of not only the exposure pathways used at calculation of the radioactivity concentration limits of waste packages for near surface disposal by Nuclear Safety Commission but also ones used at the concentration limits for intermediate depth disposal. We also assumed the capacities of the disposal facilities as 44,000 m for pit disposal and 150,000 m
for pit disposal and 150,000 m for trench disposal. The radioactivity concentrations calculated in this report is used as the reference values because the disposal site has not been decided yet. Addition to this, the radioactivity concentrations will be revised according to circumstances of development of disposal facilities and so on. In the future, we will decide the radioactivity and radioactive concentration of a waste package described in the license application documents based on the dose assessment taken into consideration the disposal site conditions.
for trench disposal. The radioactivity concentrations calculated in this report is used as the reference values because the disposal site has not been decided yet. Addition to this, the radioactivity concentrations will be revised according to circumstances of development of disposal facilities and so on. In the future, we will decide the radioactivity and radioactive concentration of a waste package described in the license application documents based on the dose assessment taken into consideration the disposal site conditions.
Hirouchi, Jun; Tokashiki, Yuji*; Takahara, Shogo; Manabe, Kentaro
JAEA-Research 2021-001, 284 Pages, 2021/03
Doses to the public are calculated with internal dose coefficients based on the publications of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in OSCAAR, which is a level 3 Probabilistic Risk Assessment code developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The gastrointestinal absorption fraction, 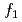 , which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that
, which is one of parameters of internal dose coefficient, is given the recommended value. However, although it has been reported that 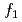 has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of
has uncertainty, the uncertainty analysis of 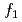 has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of
has been performed on few radionuclides. In this report, to evaluate the influence of uncertainty of 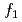 on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various
on the internal dose, we calculated the internal dose coefficient with various 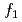 , and derive the relationship between the coefficient and
, and derive the relationship between the coefficient and 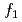 . As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
. As a result, we indicate that the relationships are expressed by a linear function for radionuclides with a half-life of more than 0.5 days and are expressed by a cubic function for radionuclides with a half-life of less than 0.5 days.
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (110), p.13 - 19, 2020/10
The article depicts how to estimate the external exposure dose for wild animals using electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. The relationship between the CO radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
radical intensity and the absorbed dose, that is, dose response curve of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed, and the detection limit of our method was estimated. The estimated detection limit of 33.5 mGy is comparable to the previously reported detection limit for human molar teeth. The external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined using this dose response curve. The estimated external exposure dose were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Koarai, Kazuma; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Osaka, Ken*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106315_1 - 106315_4, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The relationship between the CO radical intensity and the absorbed dose (dose response curve) of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed by electron spin resonance and the detection limit of our system was estimated to be 33.5 mGy, which is comparable to the detection limit for human molar teeth. Using the dose response curve, external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined. The results suggest that the external exposure dose for the wild Japanese macaques were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
radical intensity and the absorbed dose (dose response curve) of tooth enamel of Japanese macaque was observed by electron spin resonance and the detection limit of our system was estimated to be 33.5 mGy, which is comparable to the detection limit for human molar teeth. Using the dose response curve, external exposure dose for seven wild Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima prefecture were examined. The results suggest that the external exposure dose for the wild Japanese macaques were ranged between 45 mGy to 300 mGy.
Tomita, Jumpei
Bunseki, 2019(3), p.112 - 113, 2019/03
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Kazami; Okabe, Kota; Kamiya, Junichiro; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takeda, Osamu; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.314 - 318, 2016/11
The 3 GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project generates 1MW proton beam for the neutron experiments and Main ring accelerator. In case of such high intensity hadron accelerator, the most important issue is to reduce the uncontrolled loss. The beam collimation system is designed for this purpose. In the present design, the physical aperture is 1.5 times wider than the primary collimator aperture and the beam loss can be enough localized on this condition. After a startup of RCS in 2007, the collimator system of RCS worked well. But vacuum leakage occurred during the maintenance period in April, 2016. Since it was expected that the beam collimator was radio-activated very much, we took the influence of radiation into consideration and designed the collimator (ie. a remote clamp system to connect/take off it with a vacuum flange away from itself). Therefore, during the recovery work of the collimator, we were able to reduce the worker dose to less than 60 micro Sv though the collimator block had a residual dose of 40 mSv/h.
Takahara, Shogo; Iijima, Masashi; Shimada, Kazumasa; Kushida, Teruo; Shiratori, Yoshitake
JAEA-Research 2014-024, 57 Pages, 2015/01
In order to assess the doses to representative person using deterministic approach, we measured radiation dose rates and surveyed on behavioral patterns in the areas contaminated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident. Statistical analyzes were also performed to identify the characteristics of individual doses from external exposures, as well as radiation dose rates and behavioral patterns. Radiation dose rates measured in living areas distribute with lognormal form. Behavioral patterns of the populations were different corresponding to their occupation. Time spent outdoors of indoor workers were distributed in lognormal form and those of outdoor workers had the normal distribution. Multi-regression analyses were made to explore a significant relationship between individual doses and relevant contributors. These results indicated that the significant differences were given in individual doses due to the spatial differences of radiation dose rates as well as the interindividual differences of behavioral patterns. Based on the results of analyses of relevant contributors to the external exposures, deterministic dose assessment model was developed. The validity of this model was confirmed because the assessed values were higher than those measured.
Sato, Kaoru; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Endo, Akira; Ono, Koji*; Hasegawa, Takayuki*; Katsunuma, Yasushi*; Yoshitake, Takayasu*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Kai, Michiaki*
RIST News, (58), p.25 - 32, 2015/01
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) are now developing WAZA-ARI for improvement of management of exposure doses due to CT examination under the joint research with the Oita University of Nursing and Health Sciences. The trial version of WAZA-ARI has been released on 21 December 2012. In trial version, users can perform dose assessment by using organ dose database based on the average adult Japanese male (JM-103) and female (JF-103) voxel phantoms and a 4 years old female voxel phantom (UFF4). The homepage of WAZA-ARI has been accessed over 1000 times per month and 28421 times by the end of September 2014. We are developing WAZA-ARI version 2 as the extension version of dose calculation functions of WAZA-ARI. WAZA-ARI version 2 will be released by the end of March 2015. In WAZA-ARI version 2. Users can upload dose calculation results to WAZA-ARI version 2 server, and utilize improvement of the dose management of patients and the optimization of CT scan conditions.
Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Emoto, Yutaka*; Koga, Sukehiko*; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 123(3), p.337 - 344, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:91.43(Environmental Sciences)A Japanese adult male voxel (volume pixel) phantom (hereinafter referred to as the JM phantom) was constructed on the basis of CT images of a healthy Japanese adult male volunteer. Body characteristics of the JM phantom were compared with those of a voxelized MIRD5 type phantom and a Japanese adult male voxel phantom which was previously developed. The voxel size of the JM phantom is 0.98 0.98
0.98 1 mm
1 mm . The shapes of organs of the JM phantom, even for small or complicated organs, such as thyroid and stomach, are more realistically reproduced as compared with the previous Japanese voxel phantom (voxel size: 0.98
. The shapes of organs of the JM phantom, even for small or complicated organs, such as thyroid and stomach, are more realistically reproduced as compared with the previous Japanese voxel phantom (voxel size: 0.98 0.98
0.98 10 mm
10 mm ). Photon self-absorbed fractions for brain, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, thyroid and urinary bladder wall of JM were evaluated and were compared with those of the other phantoms. In consequence, it was suggested that the mass, shape and thickness of organs are important factors for the determination of self-absorbed fractions.
). Photon self-absorbed fractions for brain, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, thyroid and urinary bladder wall of JM were evaluated and were compared with those of the other phantoms. In consequence, it was suggested that the mass, shape and thickness of organs are important factors for the determination of self-absorbed fractions.
 -ray dose around a collimator at 3-GeV proton synchrotron ring of J-PARC facility
-ray dose around a collimator at 3-GeV proton synchrotron ring of J-PARC facilityNakane, Yoshihiro; Nakano, Hideo*; Abe, Teruo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 11th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-11) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Hirayama, Hideo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.498 - 501, 2004/03
JAERI-Universities Joint Research Project has been carried out to study the radiation safety in high-energy proton accelerator facilities since 2000. Ten groups from 2 research institutes and 5 universities joined in the project to tackle 3 major subjects below, using a quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at TIARA facility of JAERI. The groups had annual meetings to discuss the plan and progress of the studies and exchange their views for effective cooperation. (1)Studies on basic physical data necessary for neutron dosimetry. (2)Development of neutron monitors and dosimeters for several tens MeV region. (3)Studies on formation of radioactive aerosols and gases for internal dosimetry.
Sakai, Akihiro; Okoshi, Minoru
Radiation Risk Assessment Workshop Proceedings, p.175 - 186, 2003/00
To establish the clearance levels, the Nuclear Safety Commission (NSC) has been discussing the clearance levels since May 1997. The NSC derived the unconditional clearance levels for the solid materials, namely concrete and metal, arising from the operation and dismantling of nuclear reactors and post irradiation examination (PIE) facilities. Two destinations of the cleared materials, namely disposal and recycle/reuse, were considered. Deterministic calculation models were established to assess individual doses resulting from 73 exposure pathways, and realistic parameter values were selected considering the Japanese natural and social conditions. The clearance levels for 21 radionuclides of nuclear reactors and for 49 of PIE facilities were derived as radioactivity concentration equivalent to the individual doses of 10  Sv/y. Most of calculated clearance levels were nearly the same as those shown in IAEA-TECDOC-855. Some, however, were different. It is considered that the major reasons depend on differences of fixed scenarios and of selected values of parameters.
Sv/y. Most of calculated clearance levels were nearly the same as those shown in IAEA-TECDOC-855. Some, however, were different. It is considered that the major reasons depend on differences of fixed scenarios and of selected values of parameters.
Yanagihara, Satoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(10), p.734 - 737, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Hideo
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 8(2), p.103 - 114, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Matsuzuru, Hideo
Nihon Gakujutsu Kaigi Kohaishita Seikatsu Kankyo No Sentan Gijutsu Ni Yoru Kaifuku Kenkyu Renrakukai Iinkai Shimpojiumu "Hoshasei Busshitsu Ni Yoru Kankyo Osen No Yobo Ni Mukete", p.53 - 62, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Ryuichi; Saito, Kimiaki; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Nagaoka, Toshi
Hoken Butsuri, 36(4), p.297 - 307, 2001/12
There are many factors which affect external exposure in contaminated area: distributions of fallout, compositions of radioactive nuclides, soil conditions, depth profile of radioactivity in soil, rain fall, snow cover, radioactive decay, shielding effects of houses and other structures, de-contamination measures, and the 'occupancy factor' which accounts for the fraction of time that inhabitants spend in different locations. In this study, several important issues concerning these factors have been investigated using field measurements and computational simulations since 1992 in the Chernobyl area. The objectives of the study were: (1) The development of a mobile survey method to collect radiation data of the contaminated area over a wide area in a short time; (2) The verification of a method to infer external doses to the population; (3) The provision of basic data used for the evaluation of external dose due to gamma ray using a Monte Carlo simulation method. (4) Characteristics of the radiation fields in contaminated area. In this report, the results were summerized.